
With my varied professional background, I am uniquely suited for cross-disciplinary work. Experience in ecology, toxicology, infectious disease microbiology, and RNA helps me elucidate trends on multiple levels of biological organization and collaborate with scientists in many different fields. Creativity and a willingness to take on high-risk / high-reward projects drives my science.
My view has always been “run the experiment and find out!” Emerging technology is a space for my experimentation. Tech such as next-generation sequencing has revolutionized biology from a data poor to a data rich field; since I’m excited to implement cutting-edge techniques I have been supplementing wet lab work with bioinformatics.
My thesis work bridges fundamental molecular biology and clinical applications. Asking research questions with the potential to affect the most vulnerable members of society, I have always approached science as public service. As a non-traditional scientist, it’s easy to think outside the currently accepted paradigms!
Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Filamentation in Candida albicans
Candida albicans poses an increasing threat to human health. C. albicans lives as a commensal of the skin, gastrointestinal system, and urogenital tract in healthy humans. However, this opportunistic organism infects immunocompromised individuals via the blood (candidemia) and deep-seated candidiasis. Candidemia is the fourth most common nosocomial disease, causing 250,000 infections and 50,000 deaths annually. As the immunocompromised population grows, more individuals will be vulnerable to C. albicans infection in the future. The poor prognosis of candidemia is due to diagnostic challenges, low drug efficacy, severe side effects, and increasing antifungal resistance. In addition to propagating antifungal resistance – human activities such as climate change, habitat destruction, and globalization all contribute to the ubiquitous escalation of fungal pathogens. Developing novel diagnostics and therapeutics requires thorough insight into fundamental molecular mechanisms of C. albicans pathogenicity.
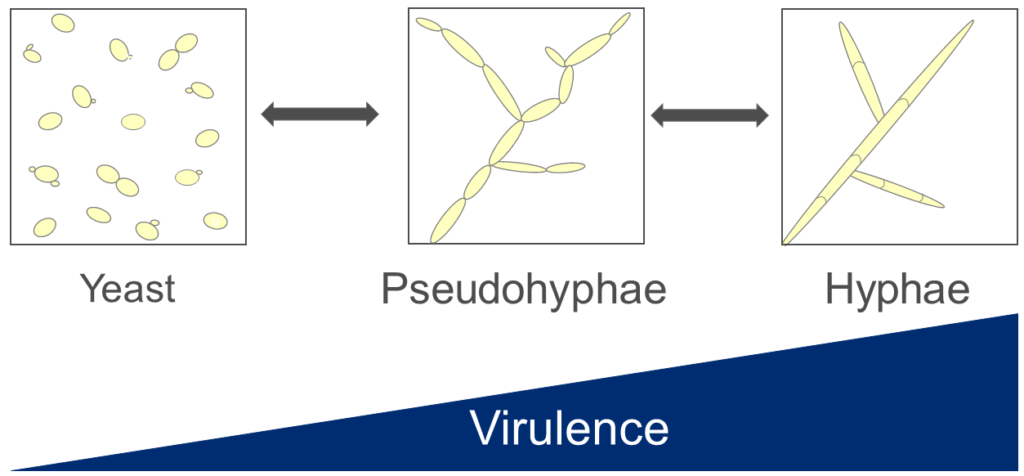
C. albicans’ ability to detect, respond, and survive stressors in highly divergent physiological microenvironments is required for pathogenicity. In response to combinatorial stressors, C. albicans undergoes a reversible morphological shift from benign round yeast to pathogenic branching hyphae in a process called filamentation. Hyphae are primarily responsible for virulence. While transcriptional regulation of stress-induced filamentation in C. albicans is well established, post-transcriptional mechanisms remain relatively unexplored. Many organisms, including the fungal pathogen C. neoformans, utilize post-transcriptional regulation to rapidly reprogram the translatome, upregulating translation of stress response genes and silencing housekeeping genes, suggesting a role for post-transcriptional regulation in C. albicans filamentation.
My thesis work explores mRNA translation and localization during filamentation. Specifically I will address the role of alternative 5’ transcript leaders in translation initiation and localization of mRNA transcripts to stress granules and P-bodies. As such, elucidating the extent of post-transcriptional control in C. albicans filamentation, could contribute to the development of desperately needed novel therapeutics to address the growing threat of candidiasis and rapid diagnostics discerning commensal colonization vs. pathogenic infection. Additionally, my thesis would contribute to basic science, establishing C. albicans as tractable model organism for elucidating the fundamental biology of post-transcriptional regulation in dimorphic fungi.
HIV-1 Diagnostics and Persistence
Untreated HIV-1 invariably results in plasma viremia, AIDS and death. Treatment with modern combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) suppresses plasma viremia below the limit of detection (LoD) of available commercial HIV-1 RNA assays, but ART does not eliminate viremia or cure HIV-1 infection. Cessation of ART inevitably leads to viral rebound.
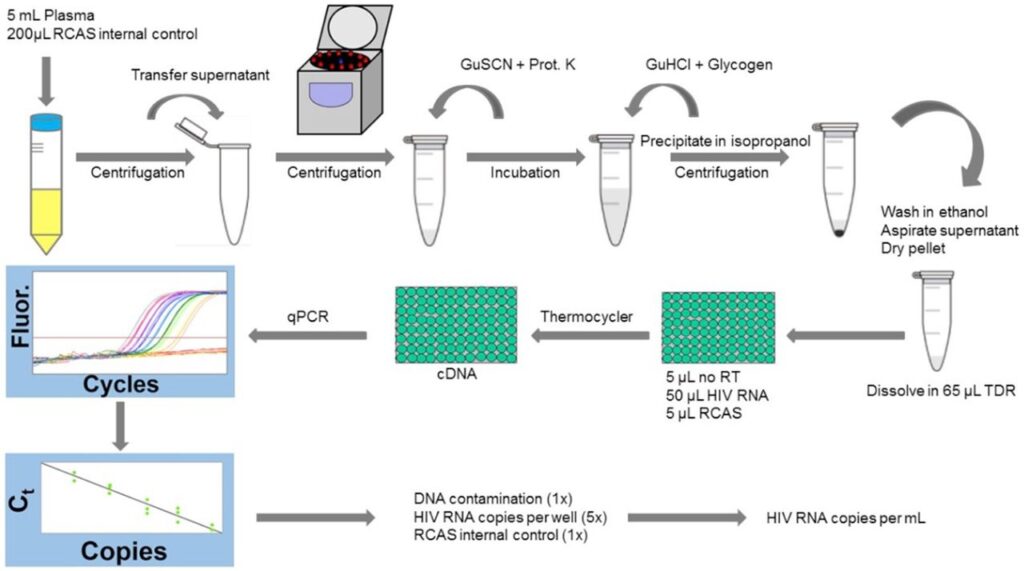
The prior generation of qRT-PCR assay targeted a highly conserved region of integrase in HIV-1 pol (integrase Single Copy Assay, iSCA). However, iSCA was limited by ultracentrifugation (cost and throughput issues) and sacrificing about half of the total extracted RNA for controls. My developmental contributions to iSCA v. 2.0 replaced the ultracentrifuge with a tabletop microcentrifuge and tested over three-fourths of the extracted nucleic acid for HIV-1 RNA while maintaining controls.
Compared to iSCA; iSCA v. 2.0 has a lower LoD, less startup costs, and simpler sample processing making it accessible to labs around the world. As long-term ART suppresses viremia below the LoD of FDA licensed clinical assays, more sensitive assays are needed in research settings, especially for studies of persistent low level viremia and curative interventions.
Nanotoxicology
The unique physical properties of nanomaterials has led to their exponential use in manufacturing settings. However, new nanomaterial development is outpacing research on health risks of these new materials. To assess a method for complex nanomaterial exposure in a mixed dust manufacturing setting, I sampled the air in tire manufacturing facilities where carbon black (CB) and amorphous silica (AS) were the primary fillers. A Dekati Low Pressure Impactor (DLPI) collected air samples during mixing, which were analyzed via scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) coupled with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) to identify the fraction of nano-scale particles (CB, AS, or ‘other’). My group identified that approximately 95% of all nanoscale particles from these tire manufacturing facilities were CB or AS and that this method may be used to estimate worker exposure to nanomaterials even in environments with diverse particle types.
Swine CAFOs & Adverse Birth Outcomes
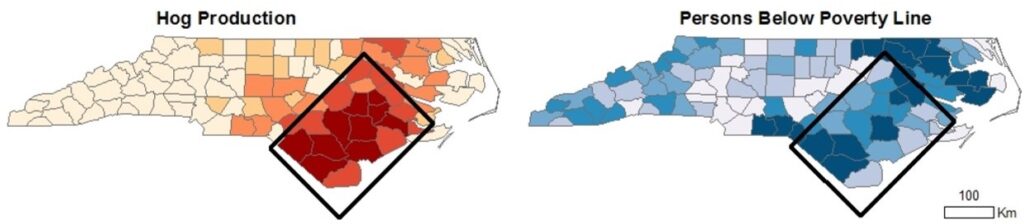
Confined Animal Feeding Operations (CAFOs) present multiple health risks to local communities. For my master’s thesis, I used geographic information systems (GIS) to map disparities in community burden of swine CAFOs and adverse pregnancy outcomes in North Carolina. Swine CAFOs were more likely to be located in communities already facing multiple disparities. Using ordinary least squares regression modeling, I demonstrated a statistically, but not clinically significant association between exposure to swine CAFO emissions and birth weight. Due to compounding stressors faced by pregnant rural women of color, swine CAFOS pose a significant environmental justice issue in North Carolina.
Fish Histology
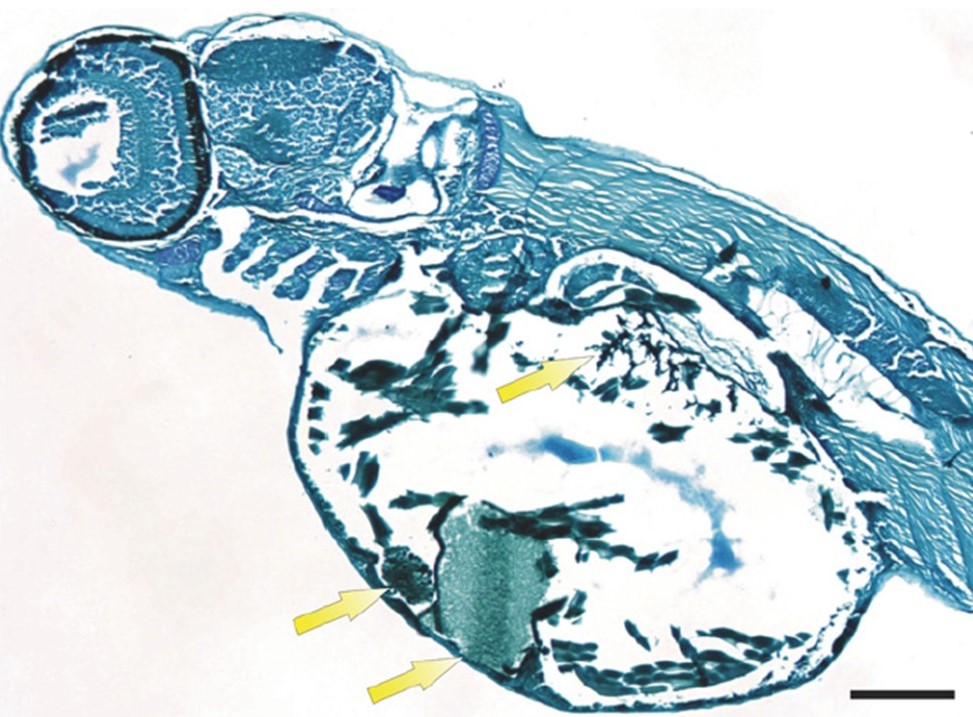
Hepatic lipidosis is a non-specific biomarker of pollution exposure in fish. However, it is often overlooked due to challenges in staining lipids. I modified an osmium tetroxide staining technique which preserved lipids in hepatic fish tissue permitting visualization. This technique may be applied to survey wild fish for environmental toxicity or laboratory for toxicity testing.
Anti-Microbial Consumer Goods

An increasing number of antimicrobial goods are available to the general public. I found that polyurethane keyboard covers impregnated with an antimicrobial polymer reduced viability of MRSA, VREF, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa. Furthermore, I found that an alcohol based hand wipe was more effective in reducing the carriage of S. marcescens compared to an alcohol based gel.
Let's Work Together
If you are interested in learning more about my current and past research, or collaborating, let’s connect!
